- 1. Understanding Knee Joint Anatomy and Function
- 2. Common Causes of Knee Joint Pain and Degeneration
- 2025. Embracing New Technologies for Knee Joint Support
1. Understanding Knee Joint Anatomy and Function
1.1 Basic Anatomy of the Knee
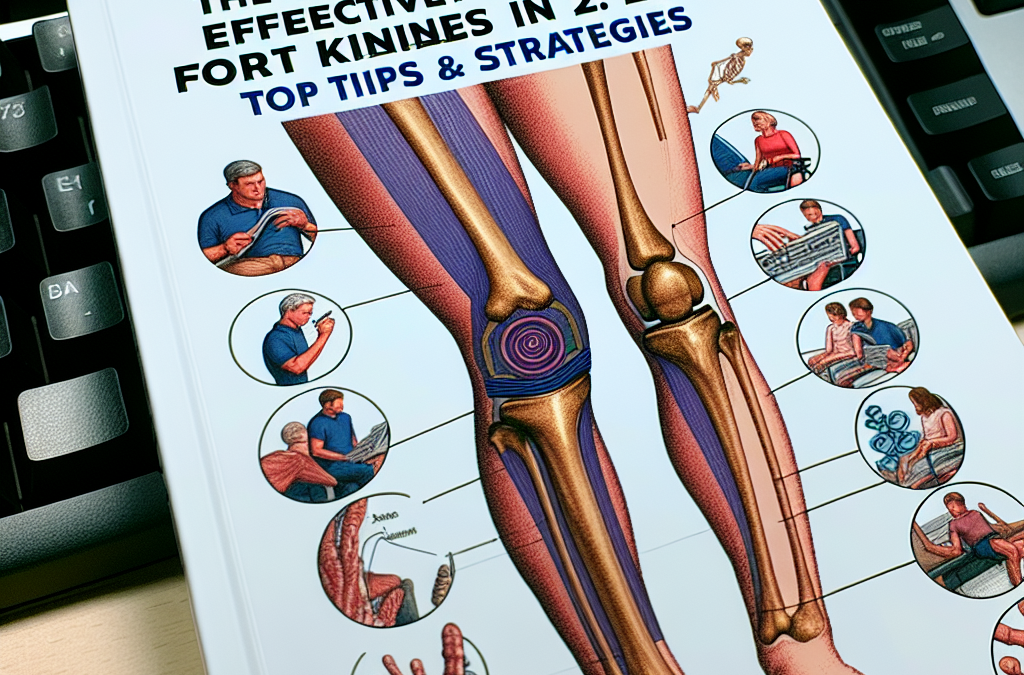
The knee joint is one of the most complex and vital joints in the human body. Comprised of bones, cartilage, ligaments, and muscles, it enables us to walk, run, and perform various daily activities. In 2025, understanding the intricacies of knee anatomy remains essential for effective joint support for knees. Knowing the roles each component plays helps us tailor strategies for injury prevention and rehabilitation.
Specifically, the femur (thigh bone), tibia (shin bone), and patella (kneecap) form the core of the knee structure. These bones are connected via ligaments that provide stability, such as the ACL and PCL. Cartilage acts as a cushion, reducing friction during movement. As we age or due to injury, damage to any of these parts can impair joint function.
By understanding the basic anatomy, individuals can better recognize symptoms of knee issues and seek targeted solutions. This foundational knowledge is key to supporting the knees effectively in 2025.
The Best Joint Support (Naturally) Starts with Organic Nutritional Support!
Get 40% Off Here ...
1.2 How the Knee Functions During Movement
The knee functions as a hinge joint, allowing flexion and extension essential for walking, running, and jumping. It also provides slight rotational movement for stability and adaptability. Understanding this function helps in designing joint support for knees that accommodates movement needs while minimizing strain.
In 2025, advanced biomechanical research sheds light on how different activities influence knee wear and tear. For example, repetitive squatting or high-impact sports can accelerate cartilage breakdown if not properly supported. Injury prevention involves understanding these movements and employing appropriate protective strategies.
Supporting the knee during daily and athletic activities involves strengthening surrounding muscles like the quadriceps and hamstrings, which absorb stress and reduce joint pressure. Maintaining this balance is a cornerstone of effective joint support for knees.
2025. Embracing New Technologies for Knee Joint Support
2025.1. Cutting-Edge Biomechanical Devices
This year, innovative biomechanical devices, such as smart knee braces equipped with sensors, offer real-time feedback on joint stress levels. These tools enable users to correct movement patterns before injury or pain worsens, enhancing joint support for knees effectively.
Examples include wearable tech that monitors gait and provides recommendations for posture correction. Integrating these with smartphone apps allows users to track progress and adjust activities accordingly. Such technology is revolutionizing preventive care and rehabilitation for knee health.
Practical use involves working with healthcare professionals to select appropriate devices tailored to individual needs, particularly for athletes or those recovering from injury. These advancements in 2025 promise safer, more personalized joint support strategies.
2025.2. Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Therapies
Regenerative medicine is making significant strides in 2025, offering hope for those with degenerated knee joints. Stem cell therapies are being used to promote cartilage regeneration and reduce inflammation, signing a new era in joint support for knees.
Patients considering these treatments should consult specialists to understand the benefits and limitations. While still evolving, research indicates promising outcomes in restoring joint function, potentially delaying or even avoiding the need for surgery.
These therapies underscore the importance of early intervention and ongoing support, emphasizing integrative approaches that combine physical therapy, lifestyle adjustments, and advanced treatments.
Conclusion
In 2025, effective joint support for knees remains a blend of foundational knowledge, personalized strategies, and cutting-edge technology. By understanding knee anatomy and function, addressing common causes of pain, and embracing innovations like regenerative medicine and smart devices, individuals can maintain healthy knees well into the future. Whether you’re an athlete, a senior, or someone recovering from injury, prioritizing support for your knees today is essential for a vibrant, active life tomorrow. Remember, proactive care and staying informed are your best tools for lasting knee health in 2025 and beyond.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the best supplements for joint support for knees in 2025?
In 2025, supplements like glucosamine, chondroitin, omega-3 fatty acids, and collagen peptides are popular for supporting knee health. Emerging research also highlights the benefits of turmeric and curcumin for reducing inflammation. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting new supplements.
2. How can I prevent knee injuries during sports?
Prevention involves proper warm-up routines, strength training for supporting muscles, and wearing suitable footwear. Incorporating flexibility exercises like yoga or stretching can also help maintain joint health and prevent injuries.
3. Is joint support for knees effective without surgery?
Absolutely. Non-surgical approaches such as physical therapy, lifestyle modifications, proper nutrition, and technological aids can significantly improve knee support and reduce pain without invasive procedures.
4. How does aging affect joint support for knees?
Aging often leads to cartilage wear, decreased muscle strength, and inflammation. Consistent support strategies, including exercise, nutrition, and possibly regenerative therapies, can mitigate age-related decline and promote healthy joint function.
5. What new advances are expected in joint support for knees in 2025?
In 2025, innovations like wearable biomechanical sensors, regenerative medicine, and personalized rehabilitation programs are transforming how we support knee health. Staying updated with these technologies can enhance long-term joint support strategies.